It’s the time of the year to usher out the old and ring in the new. New Year’s Eve is a hopeful, joyous night as we look forward to ushering in 12 months of prosperity. It’s a night of celebration and we wanted to discover how various countries around the world celebrate their traditions. We found a great piece on unique customs from eating 12 grapes in Spain, shattering dishes in Denmark, burning scarecrows to cleanse the passing year’s evil, wearing red underwear to smashing pomegrantes in Greece we enjoyed reading “20 Unique New Year’s Eve Traditions from around the World” on BestLifeonline.com. We hope you have fun reading it and hopefully find additional ways to ring in the year.
FROM DRINKING ASHES TO SMASHING POMEGRANATES, THIS IS HOW OTHER COUNTRIES USHER IN THE NEW YEAR.

DECEMBER 31, 2020

New Year’s Day may start the second the clock strikes midnight on January 1 in most countries, but the celebrations undertaken to usher in the new year at different corners of the globe couldn’t be more unique. Take Ecuador, for instance: There, citizens parade around the city with scarecrows built to look like popular politicians and cultural icons—and at the stroke of midnight, said scarecrows are burnt to a crisp to cleanse the new year of everything evil. And in Brazil, it’s customary to light candles and throw white flowers into the water as an offering for Yemoja, the Queen of the Ocean. Herein, we’ve traveled the world—virtually, at least—to round up some of the most creative and culturally unique New Year’s Eve traditions from around the world. Keep reading to find out how other countries will be celebrating, and for advice on keeping your promise to yourself, check out The Biggest New Year’s Resolution Mistake Everyone Makes.
Spain: Eating Grapes For Good Luck
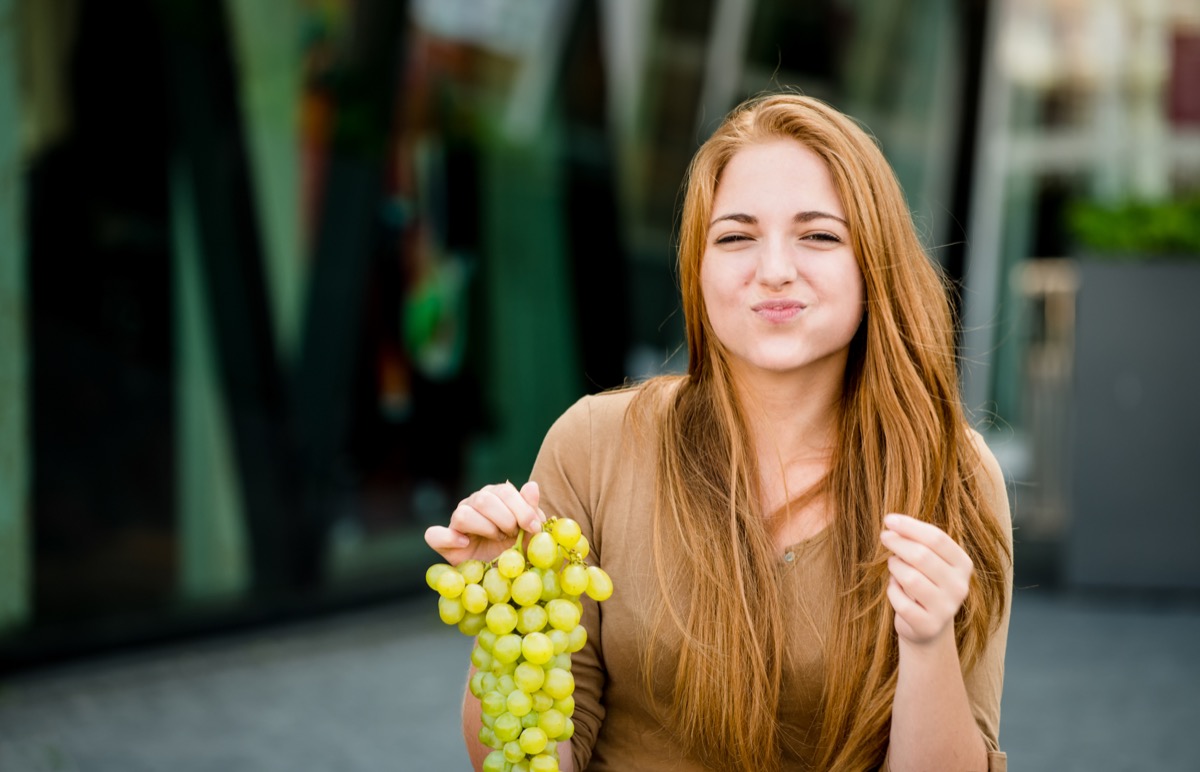

In Spain, locals will eat exactly 12 grapes at the stroke of midnight to honor a tradition that started in the late 19th century. Back in the 1800s, vine growers in the Alicante area came up with this tradition as a means of selling more grapes toward the end of the year, but the sweet celebration quickly caught on. Today, Spaniards enjoy eating one grape for each of the first 12 bell strikes after midnight in the hopes that this will bring about a year of good fortune and prosperity. For more fascinating trivia, check out 50 Most Interesting Facts About the World.
Scotland: First Footing

In Scotland, the day before January 1 is so important that there’s even an official name for it: Hogmanay. On this day, the Scottish observe many traditions, but easily one of their most famous is first footing. According to Scottish beliefs, the first person who crosses through the threshold of your house after midnight on New Year’s Day should be a dark-haired male if you wish to have good luck in the coming year. Traditionally, these men come bearing gifts of coal, salt, shortbread, and whiskey, all of which further contribute to the idea of having good fortune. But why dark-haired men? Well, back when Scotland was being invaded by the Vikings, the last thing you wanted to see at your doorstep was a light-haired man bearing a giant axe. So today, the opposite—a dark-haired man—symbolizes opulence and success.
The Netherlands: Chowing Down On Oliebollen
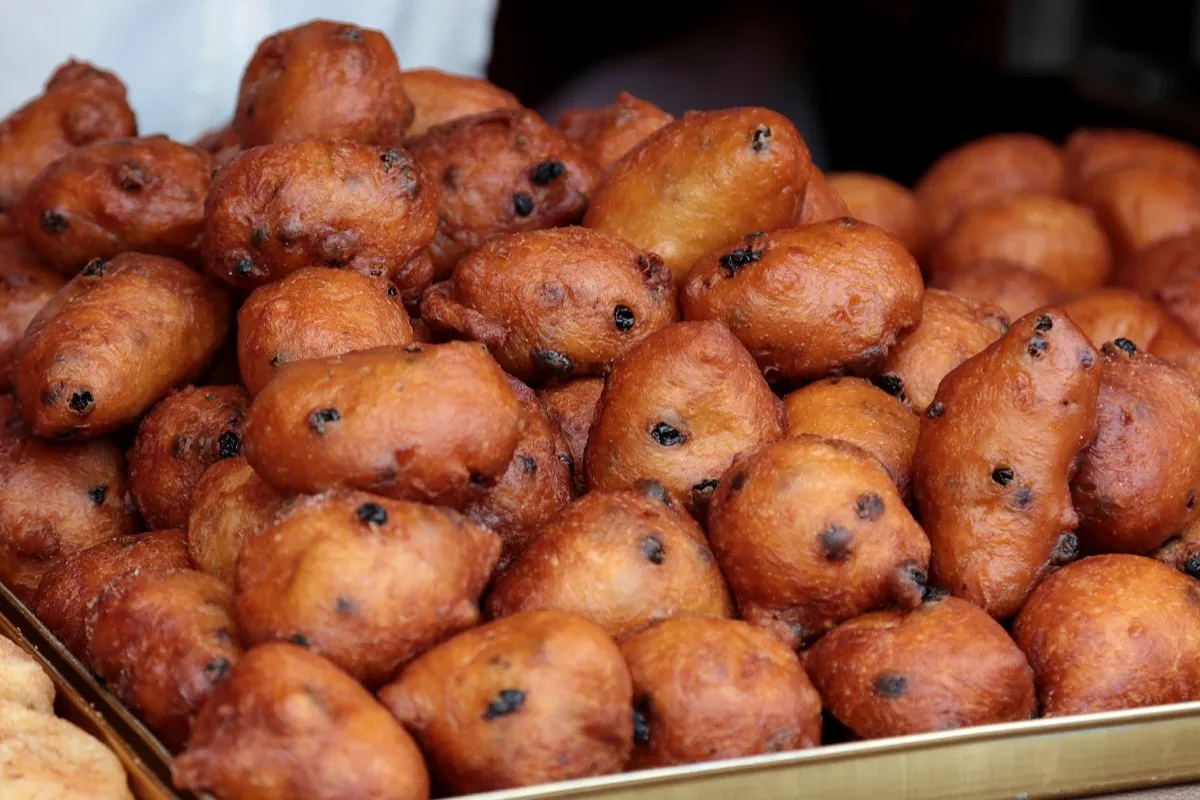

The reasoning behind this Dutch New Year’s Eve tradition is slightly odd, to say the least. Ancient Germanic tribes would eat these pieces of deep-fried dough during the Yule so that when Germanic goddess Perchta, better known as Perchta the Belly Slitter, tried to cut their stomachs open and fill them with trash (a punishment for those who hadn’t sufficiently partaken in yuletide cheer), the fat from the dough would cause her sword to slide right off. Today, oliebollen are enjoyed on New Year’s Eve, and you’d be hard-pressed to find a Dutch food vendor in the winter months who isn’t selling these doughnut-like balls. For more wisdom to share with your friends, check out 125 Facts That Will Make You Feel Instantly Smarter.
Russia: Planting Underwater Trees
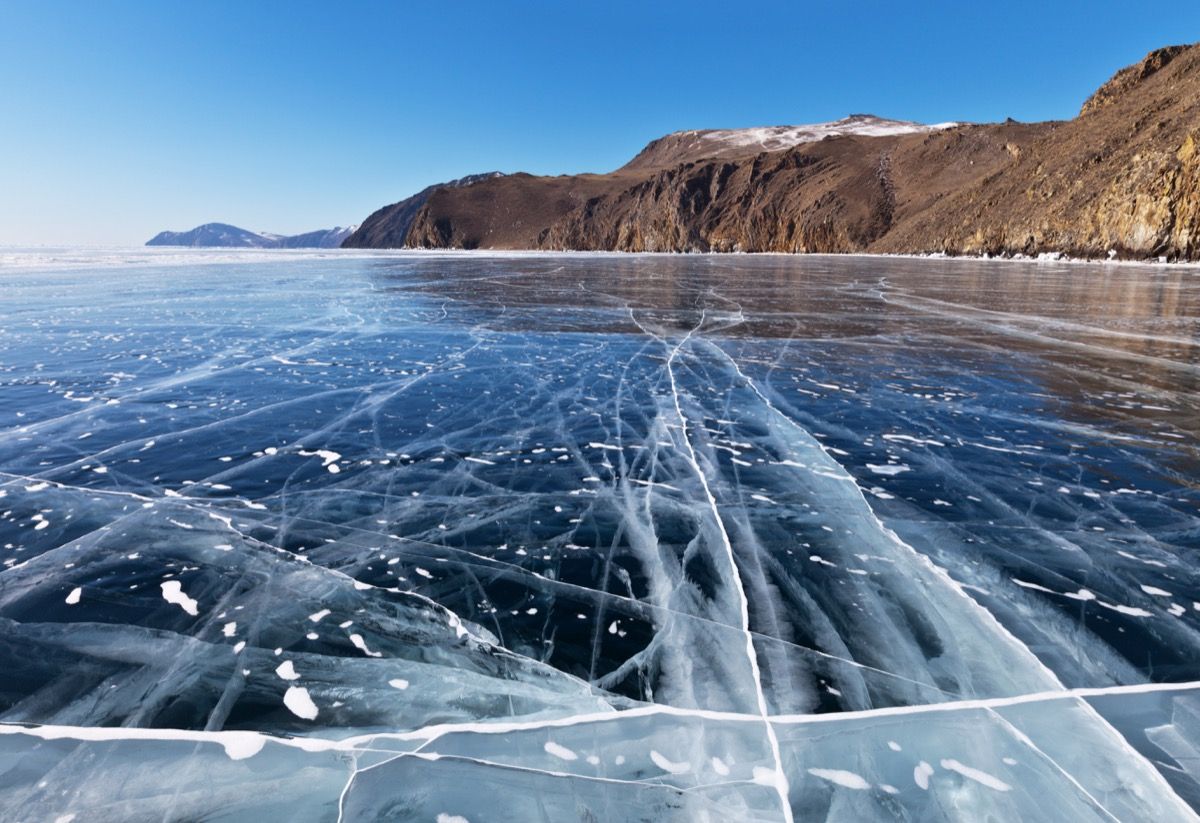

For the past 25 years or so, it has been a Russian holiday tradition for two divers, aptly named Father Frost and the Ice Maiden, to venture into a frozen Lake Baikal, the world’s largest freshwater lake, and take a New Year Tree—typically a decorated spruce—more than 100 feet below the surface. Though the temperature is normally well below freezing in Russia on New Year’s Eve, people travel from all over the world to partake in this frozen fête.
Brazil: Throwing White Flowers Into the Ocean
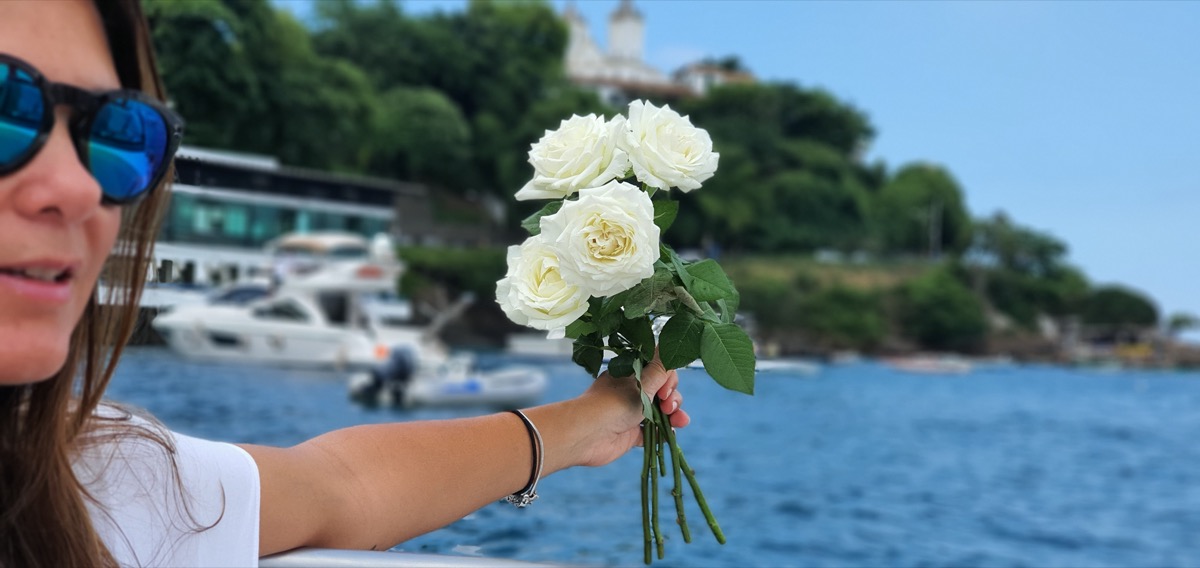

If you happen to be in Brazil for New Year’s Eve, don’t be surprised to find the oceans littered with white flowers and candles. In the South American country, it is commonplace for citizens to take to the shores on New Year’s Eve in order to make offerings to Yemoja, a major water deity who is said to control the seas, to elicit her blessings for the year to come.
Italy: Wearing Red Underwear
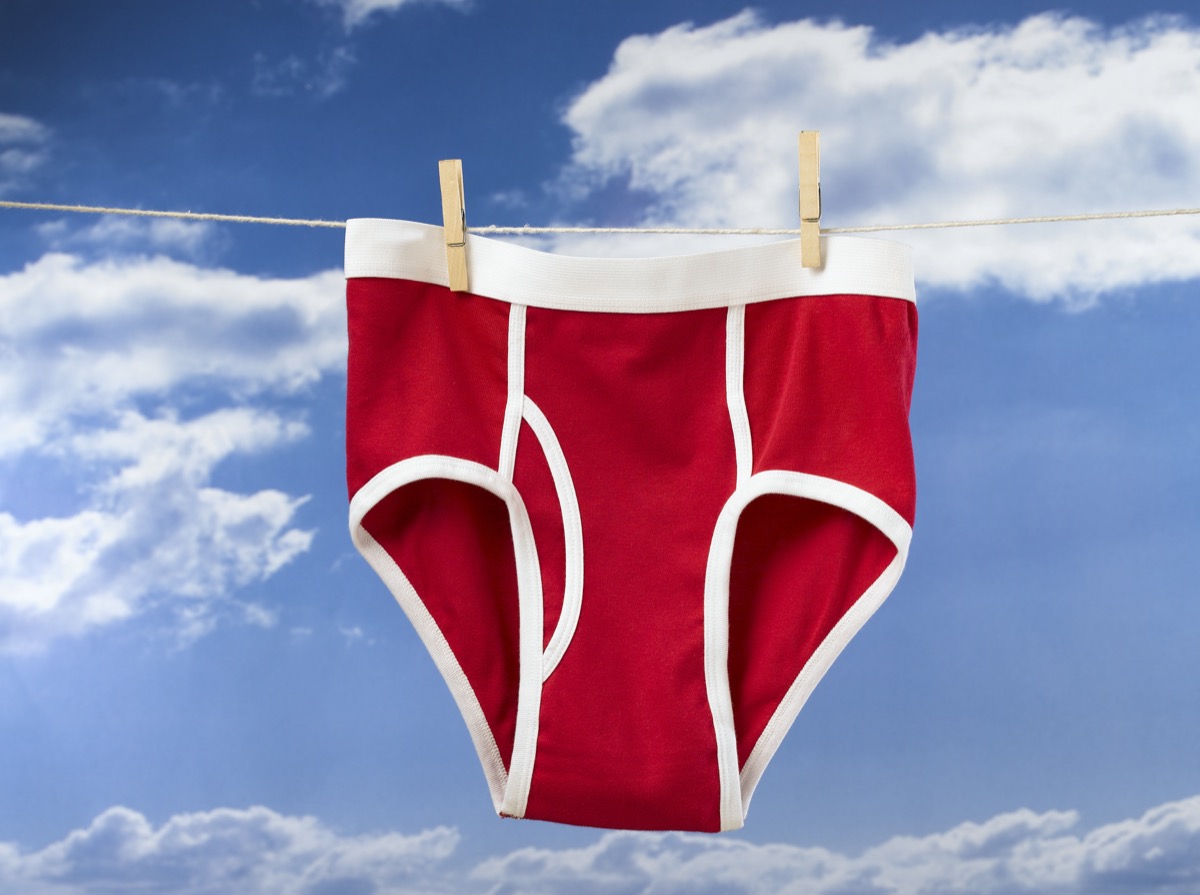

Italians have a tradition of wearing red underwear to ring in the new year. In Italian culture, the color red is associated with fertility, and so people wear it under their clothes in the hopes that it will help them conceive in the coming year.
Greece: Hanging Onions
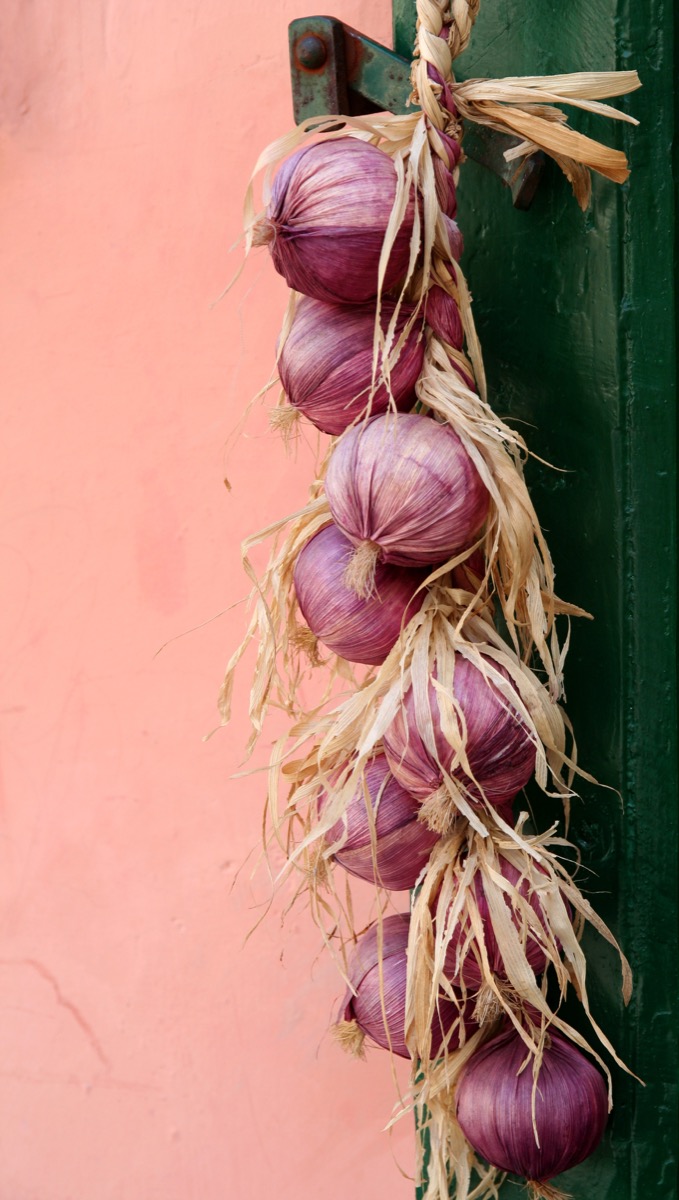

No, this New Year’s Eve tradition has nothing to do with vampires. Rather, the Greeks believe that onions are a symbol of rebirth, and so they hang the pungent vegetable on their doors in order to promote growth throughout the new year. Greek culture has long associated this food with the idea of development, seeing as all the odorous onion ever seemingly wants is to plant its roots and keep growing. And for customs that made their way to the U.S., check out 20 “American” Traditions We Totally Stole from Other Cultures.
Chile: Chilling in Cemeteries
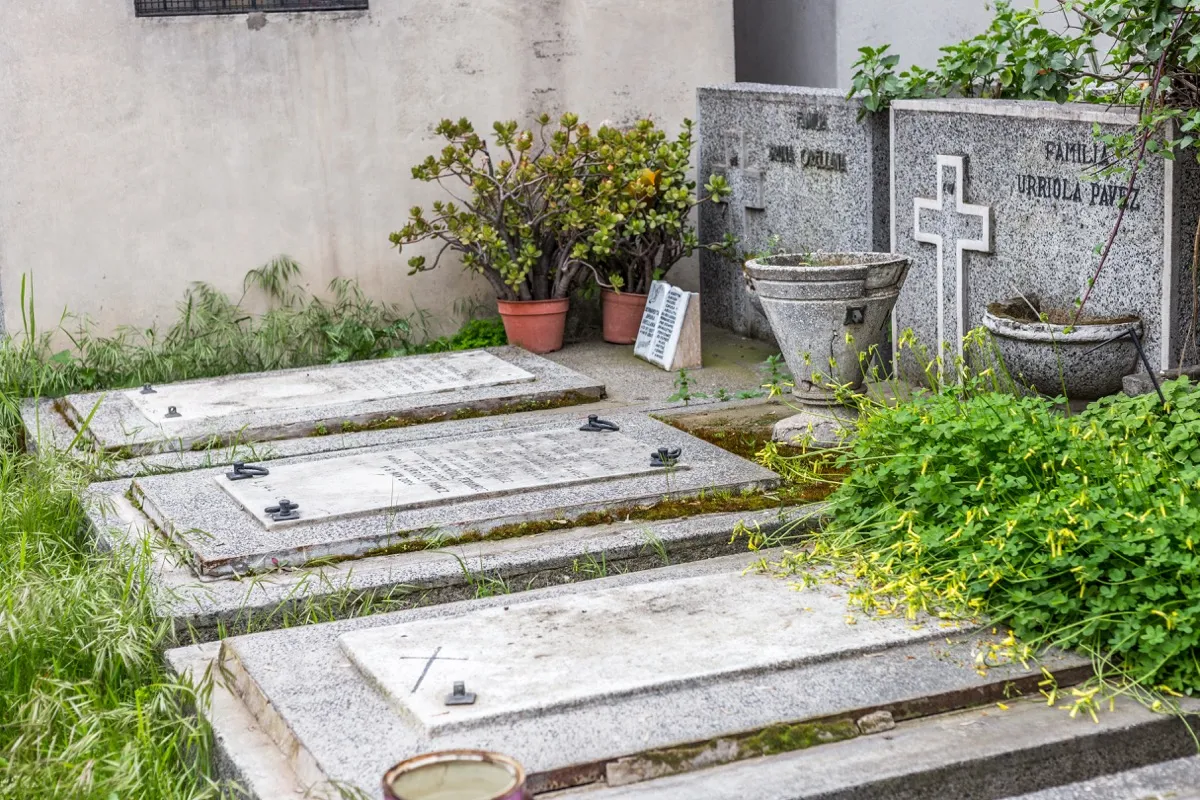

In Chile, New Year’s Eve masses are held not at church, but in cemeteries. This change of scenery allows for people to sit with their deceased family members and include them in the New Year’s Eve festivities.
Japan: Slurping Some Soba Noodles

In Japanese culture, it is customary to welcome the new year with a bowl of soba noodles in a ritual known as toshikoshi soba, or year-crossing noodles. Though nobody is entirely sure where toshikoshi soba first came from, it is believed that the soba’s thin shape and long length is meant to signify a long and healthy life. Many folks also believe that because the buckwheat plant used to make soba noodles is so resilient, people eat the pasta on New Year’s Eve to signify their strength. If you want to make a bowl of New Year’s Eve Noodles for yourself this December 31st, then check out blogger Namiko Chen‘s recipe here. And for trivia that will make you giggle, check out 40 Facts So Funny They’re Hard to Believe.
Denmark: Smashing Plates
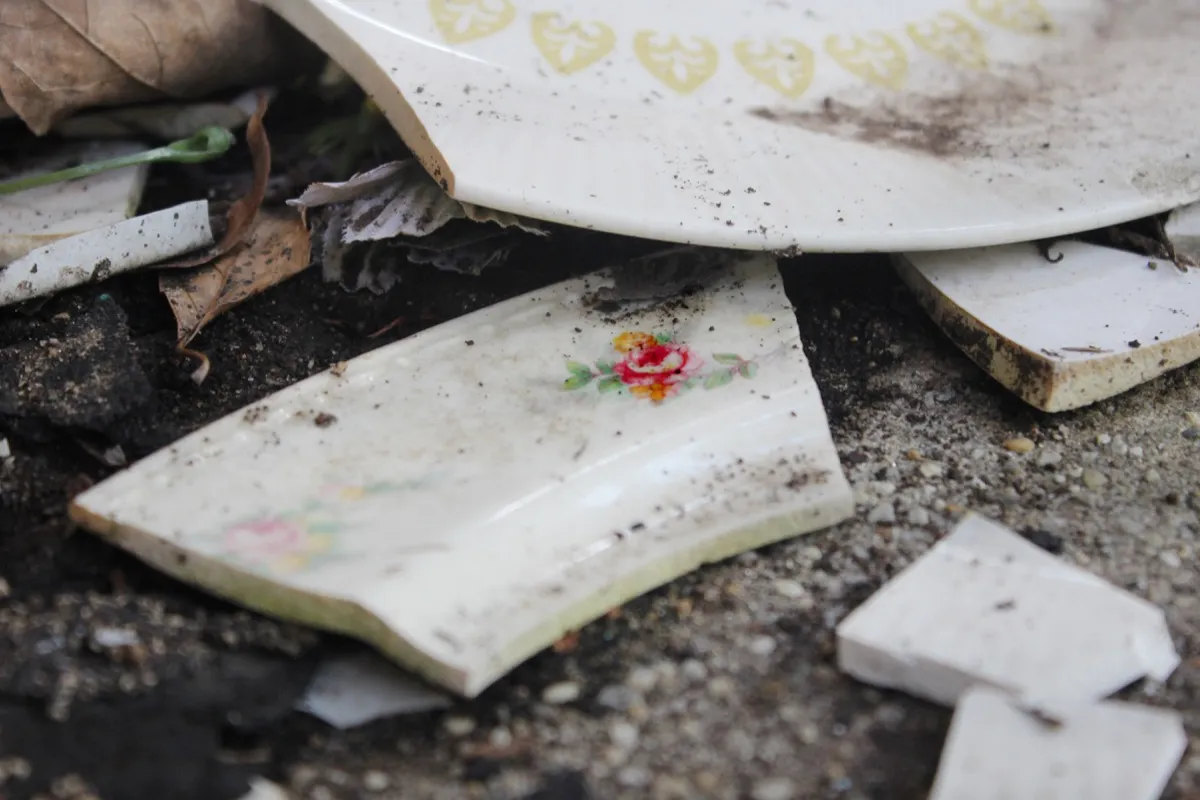

In Denmark, people take pride in the number of broken dishes outside of their door by the end of New Year’s Eve. It’s a Danish tradition to throw china at your friends’ and neighbors’ front doors on New Year’s Eve—some say it’s a means of leaving any aggression and ill-will behind before the New Year begins—and it is said that the bigger your pile of broken dishes, the more luck you will have in the upcoming year.
Ecuador: Burning Scarecrows
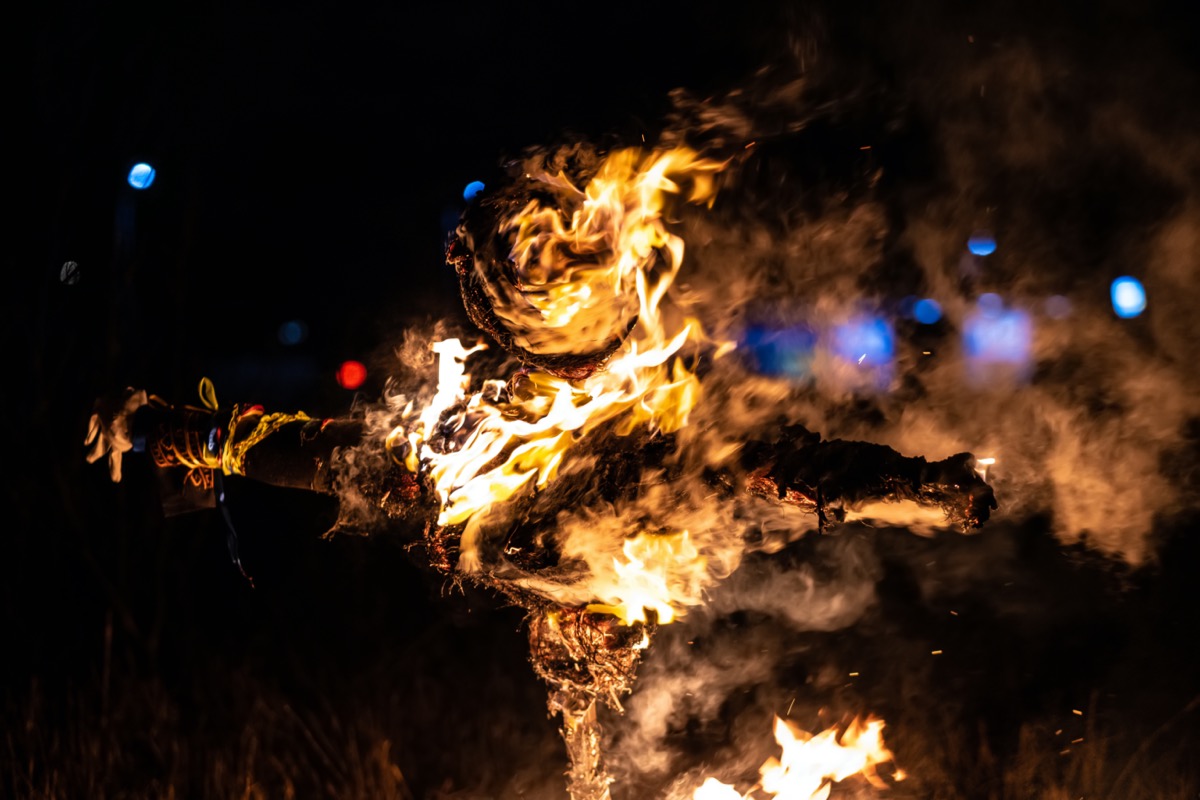
In Ecuador, New’s Year Eve festivities are lit up (quite literally) by bonfires. At the center of each of these bonfires are effigies, most often representing politicians, pop culture icons, and other figures from the year prior. These burnings of the “año viejo,” or “old year,” as they’re called, are held at the end of every year to cleanse the world of all the bad from the past 12 months and make room for the good to come.
Greece: Pummeling Pomegranates
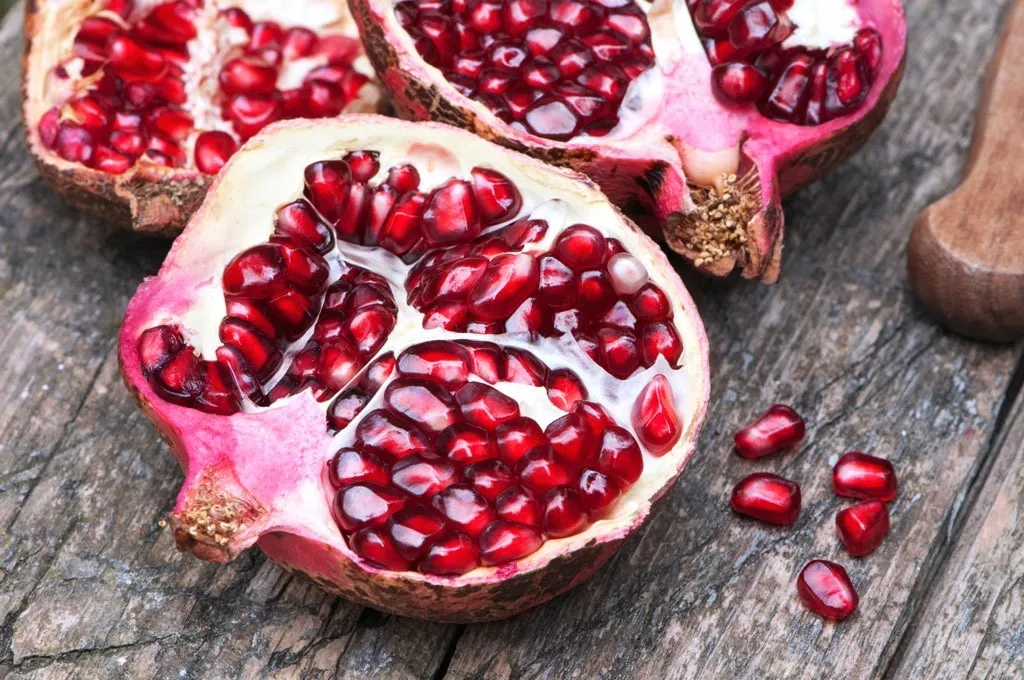

In ancient Greek mythology, the pomegranate symbolizes fertility, life, and abundance, and so the fruit has come to be associated with good fortune in modern Greece. Just after midnight on New Year’s Eve, it is customary for Greeks to smash a pomegranate against the door of their house—and it is said that the number of pomegranate seeds that end up scattered is directly correlated with the amount of good luck to come.
Germany: Pouring Lead
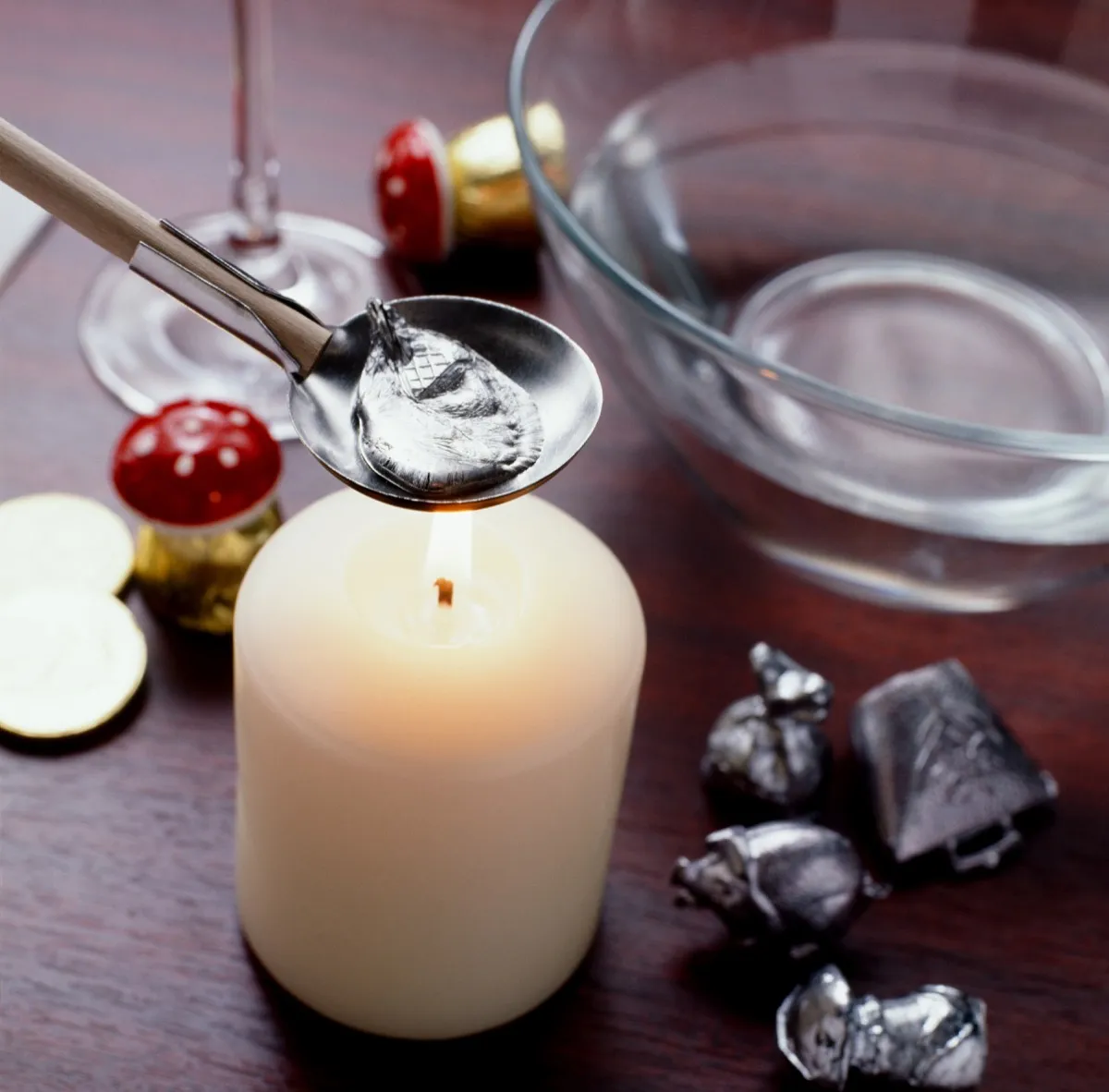

In Germany, all of the New Year’s Eve Festivities center around a rather unique activity known as Bleigießen, or lead pouring. Using the flames from a candle, each person melts a small piece of lead or tin and pours it into a container of cold water. The shape that the lead or tin forms is said to reveal a person’s fate for the upcoming year, not unlike tasseography.
Japan: Ringing Bells
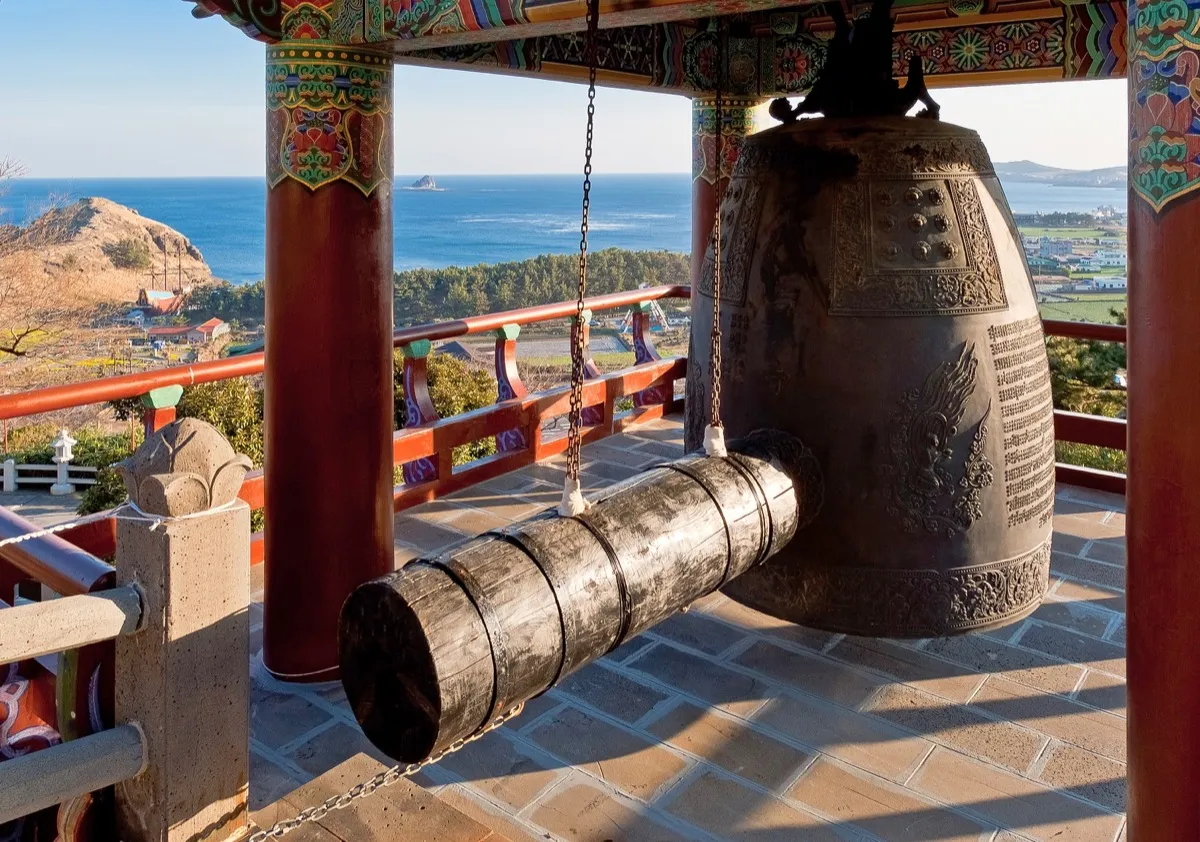

One-hundred-and-eight. That’s how many times Buddhist temples in Japan ring their bells on New Year’s Eve—107 times on New Year’s Eve, and once when the clock strikes midnight. This tradition, known as joyanokane, is meant to both dispel the 108 evil desires in each and every person and cleanse the previous year of past sins.
Russia: Drinking Ashes

Before you get grossed out, rest assured that Russians are not consuming human ashes or anything of the sort. Rather, in Russian culture, it is New Year’s Eve tradition for folks to write their wishes down on a piece of paper, burn them with a candle, and drink the subsequent ashes in a glass of champagne.
Czech Republic: Cutting Apples
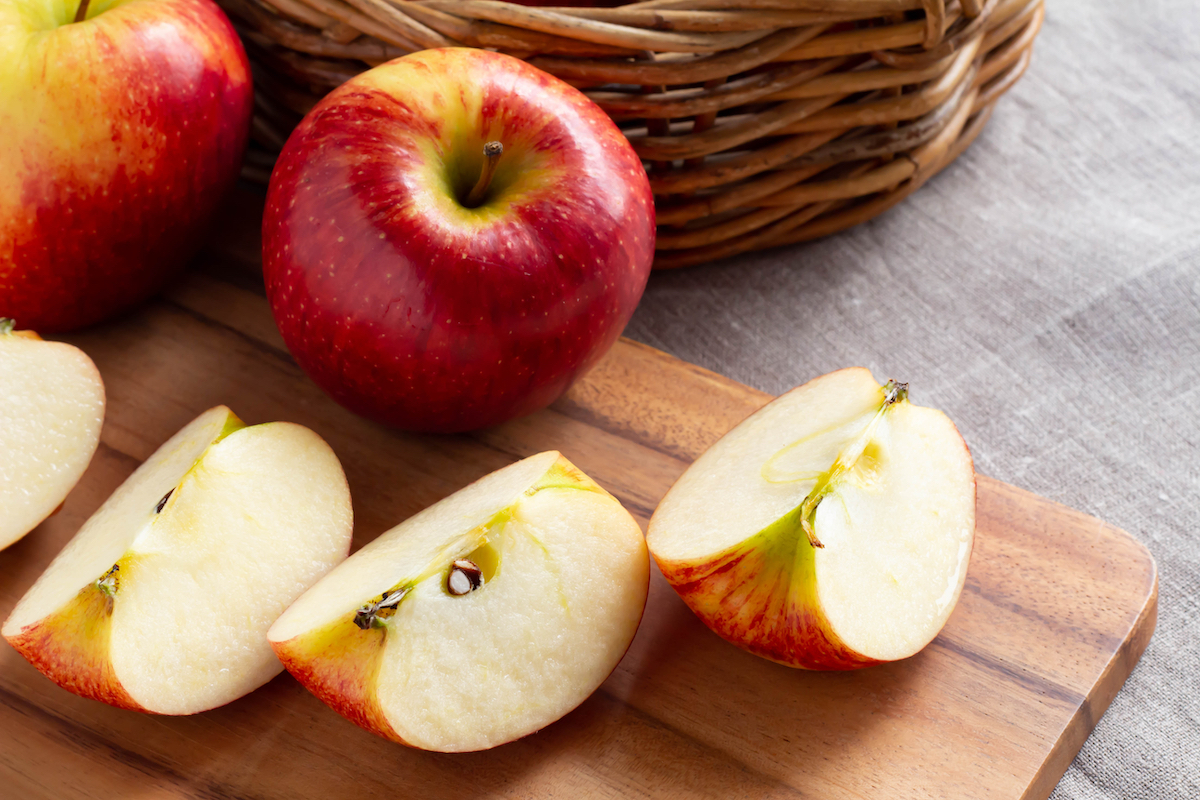

The Czech prefer to predict their future fortunes on New Year’s Eve with the assistance of an apple. The night before the new year begins, the fruit is cut in half, and the shape of the apple’s core is said to determine the fate of everyone surrounding it. If the apple’s core resembles a star, then everyone will soon meet again in happiness and health—but if it looks like a cross, then someone at the New Year’s Eve party should expect to fall ill.
Estonia: Eating Many Meals

If breakfast, lunch, and dinner are hardly enough to satiate you, then you’ll want to celebrate New Year’s Eve in Estonia. There, people believe that eating seven, nine, or 12 meals will bring about good things in the year to come, seeing as those numbers are considered lucky throughout the country. And if you can’t finish your food, worry not: People often purposefully leave food on their plates in order to feed their visiting family members—the ones in spirit form, that is.
Armenia: Baking “Good Luck” Bread
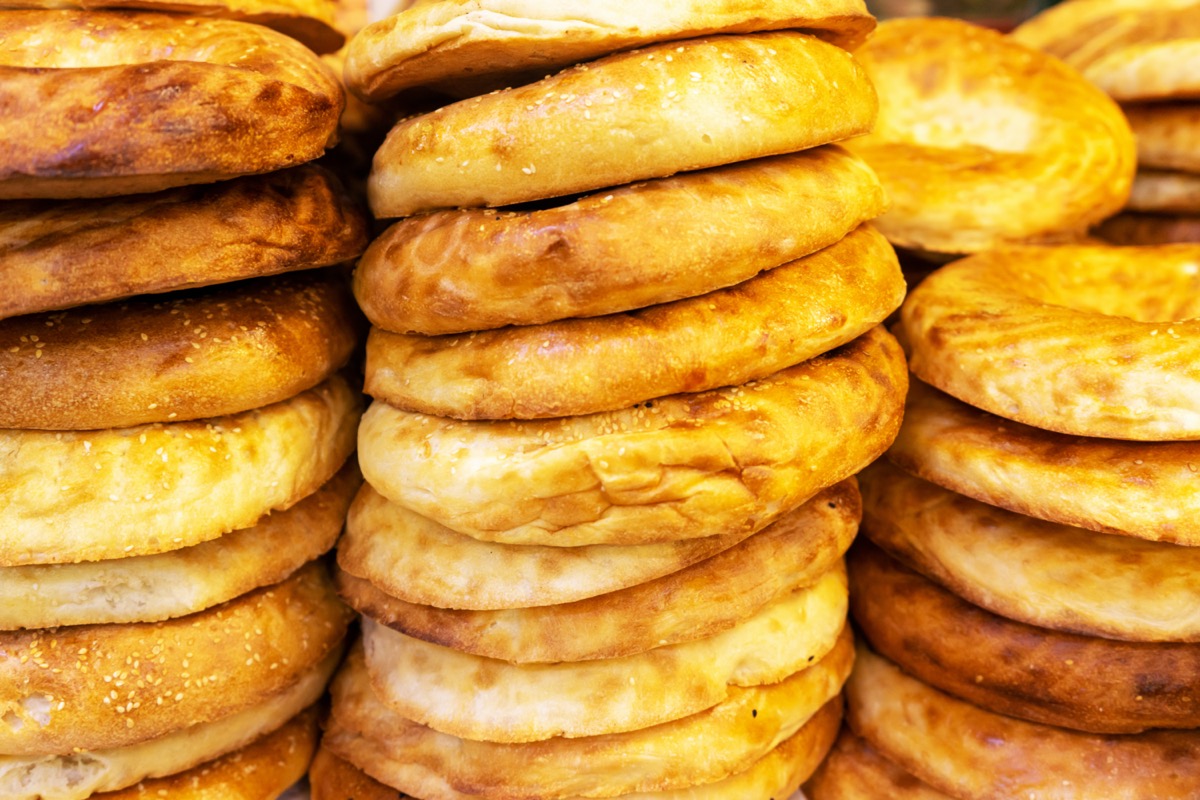

When people in Armenia bake bread on New Year’s Eve, they add a special ingredient into their dough: luck. Of course, they don’t literally add an ingredient called luck into their batter, but it is tradition for metaphorical good wishes to be kneaded into every batch of bread baked on the last day of the year.
Turkey: Sprinkling Salt
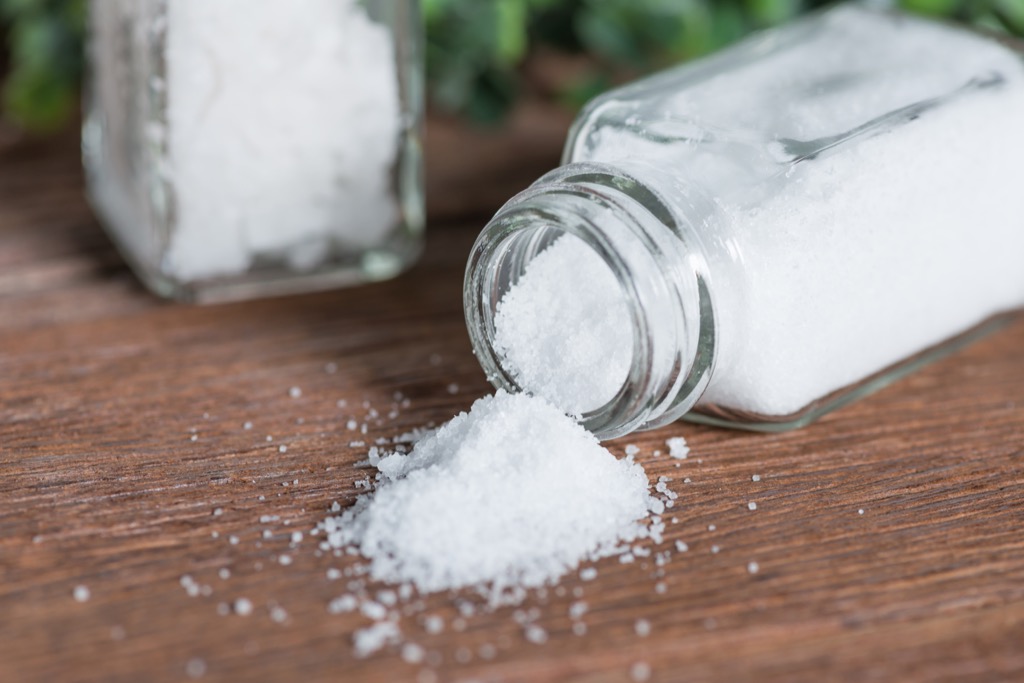

In Turkey, it’s considered good luck to sprinkle salt on your doorstep as soon as the clock strikes midnight on New Year’s Day. Like many other New Year’s Eve traditions around the globe, this one is said to promote both peace and prosperity throughout the new year.
Ireland: Sleeping on Mistletoe
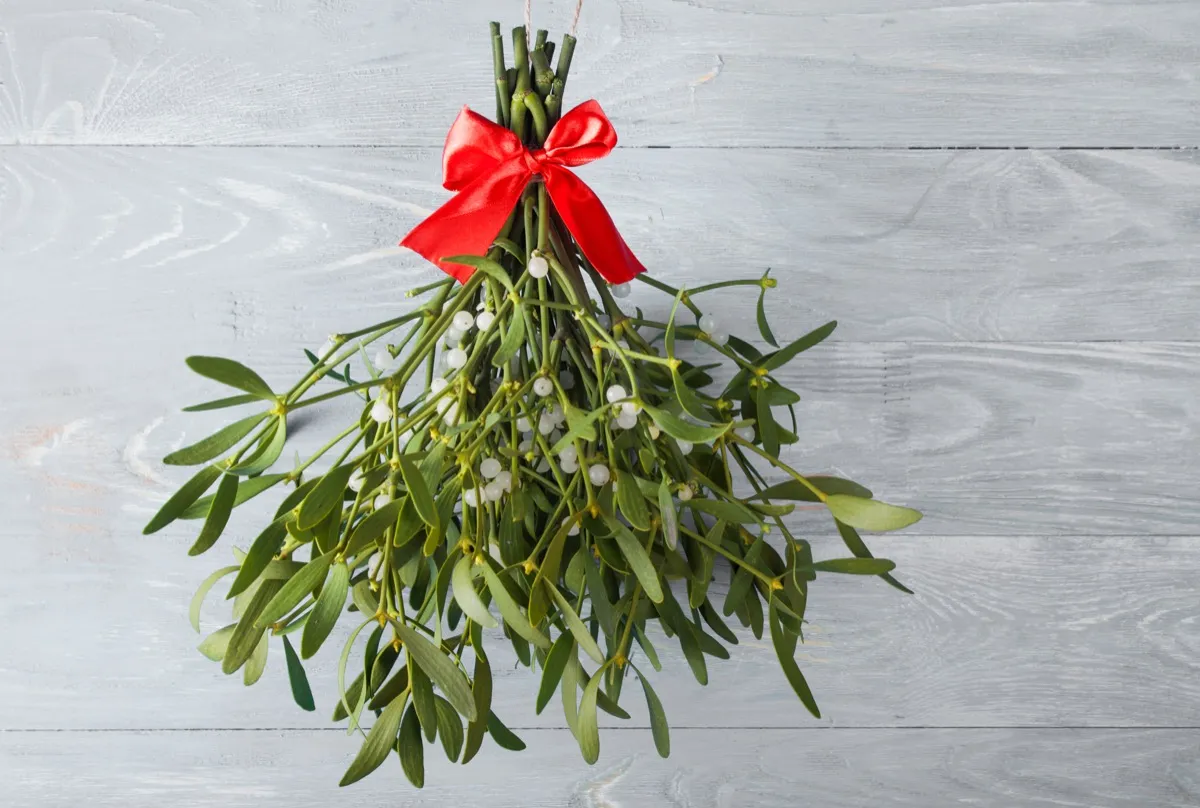

In Ireland, it’s customary for single gals to sleep with a mistletoe under their pillow on New Year’s Eve. Supposedly, sleeping with the plant helps women to find their future husbands—in their dreams, at least.

